INTRODUCTION
Viral hepatitis is inflammation of the liver caused by a germ called virus Several different viruses, named the hepatitis A, B, C, D, & E viruses, cause viral hepatitis. Hepatitis A & E cause acute or short term hepatitis Hepatitis B, C, & D viruses can also cause chronic hepatitis, in which the infection is prolonged, sometimes lifelong. Chronic hepatitis can lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer Background Information
One in every 12 persons worldwide is living with viral hepatitis; approximately 240 million persons are infected with chronic HBV & another 80 million are infected with chronic HCV infection Globally an estimated 70% of primary liver cancer and 54% of liver cirrhosis cases are caused by viral hepatitis & approximately 1.4 million deaths from viral hepatitis occur each year The proportion of persons living with viral hepatitis is greatest in Asia, sub-Saharan Africa and Egypt Nigeria accounts for 8.3% & 4.5% of the global burden of chronic HBV & HCV respectively One in every 12 persons worldwide is living with viral hepatitis; approximately 240 million persons are infected with chronic HBV & another 80 million are infected with chronic HCV infection Globally an estimated 70% of primary liver cancer and 54% of liver cirrhosis cases are caused by viral hepatitis & approximately 1.4 million deaths from viral hepatitis occur each year The proportion of persons living with viral hepatitis is greatest in Asia, sub-Saharan Africa and Egypt Nigeria accounts for 8.1% & 1.1% of 198 million Nigerians are living carriers of HBV and HCV respectively Mode of Transmission
Food or water contaminated by faeces from an infected person Exposure to infected blood, body fluids and blood products Having unprotected sex Mother to child transmission during childbirth Unsafe medical & surgical procedures Sharing of needles and other sharp objects among injection drug users Unclean tattooing and piercing Who are at Risk?
International travellers People who live with or have sex with an infected person People living in areas where children are not routinely vaccinated where outbreaks are more likely Day care children & children during outbreaks Men who have sex with men (MSMs) Haemodialysis patients immigrants and children of immigrants from areas with high rates of hepatitis B People who have multiple sex partners People who inject drugs (PWIDs) Health care workers Users of illicit drugs Infants born to infected mothers people who received a transfusion of blood or blood products before 1987 people who received a transfusion of blood or blood products before July 1992 people who received clotting factors made before 1987 What are the Signs of this Ailment/Sickness?
jaundice, which causes a yellowing of the skin and eyes fatigue abdominal pain loss of appetite Weight loss nausea vomiting diarrhoea low grade fever headache N.B: In majority of cases, everything is normal (silent killer). By the time a patient have these complaints, may mean a significant liver damage
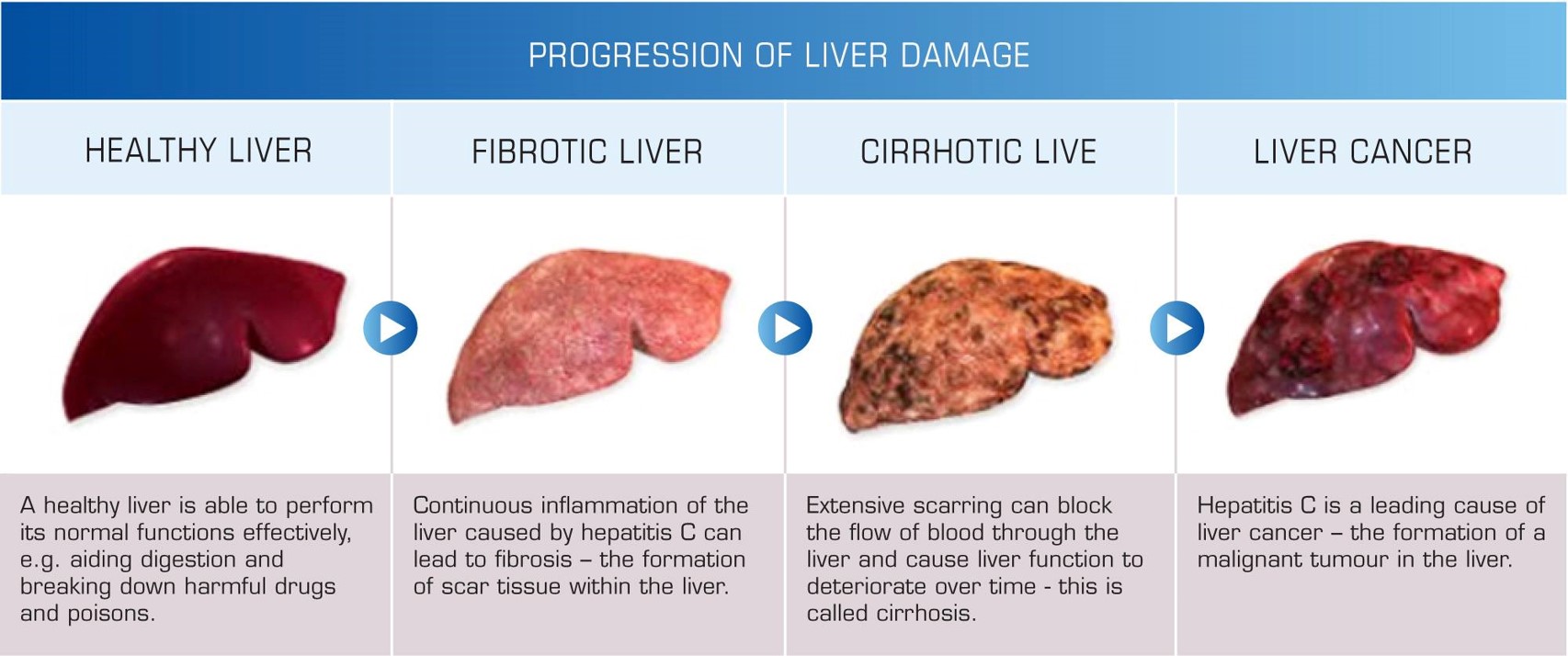
How Would You Protect Yourself & Others
Get Screened today to ascertain your status and enjoy the benefits for yourself and others Make sure your new-borns at birth are vaccinated and ensure their complete doses of vaccination for HBV As adults who test negative for HBV, ensure you get 3 doses of vaccine Refuse to take blood not Screened – Transfusion of unscreened blood is criminal As a Pregnant mother make sure you attend ante natal care and get screened for HBV Be faithful to your spouse Ensure safe injection procedure and sterilization of reusable medical equipment Avoid sharing of personal care item NB: Persons who test positive should go to the nearest health centre for proper evaluation and treatment by medical professional evaluation and treatment

